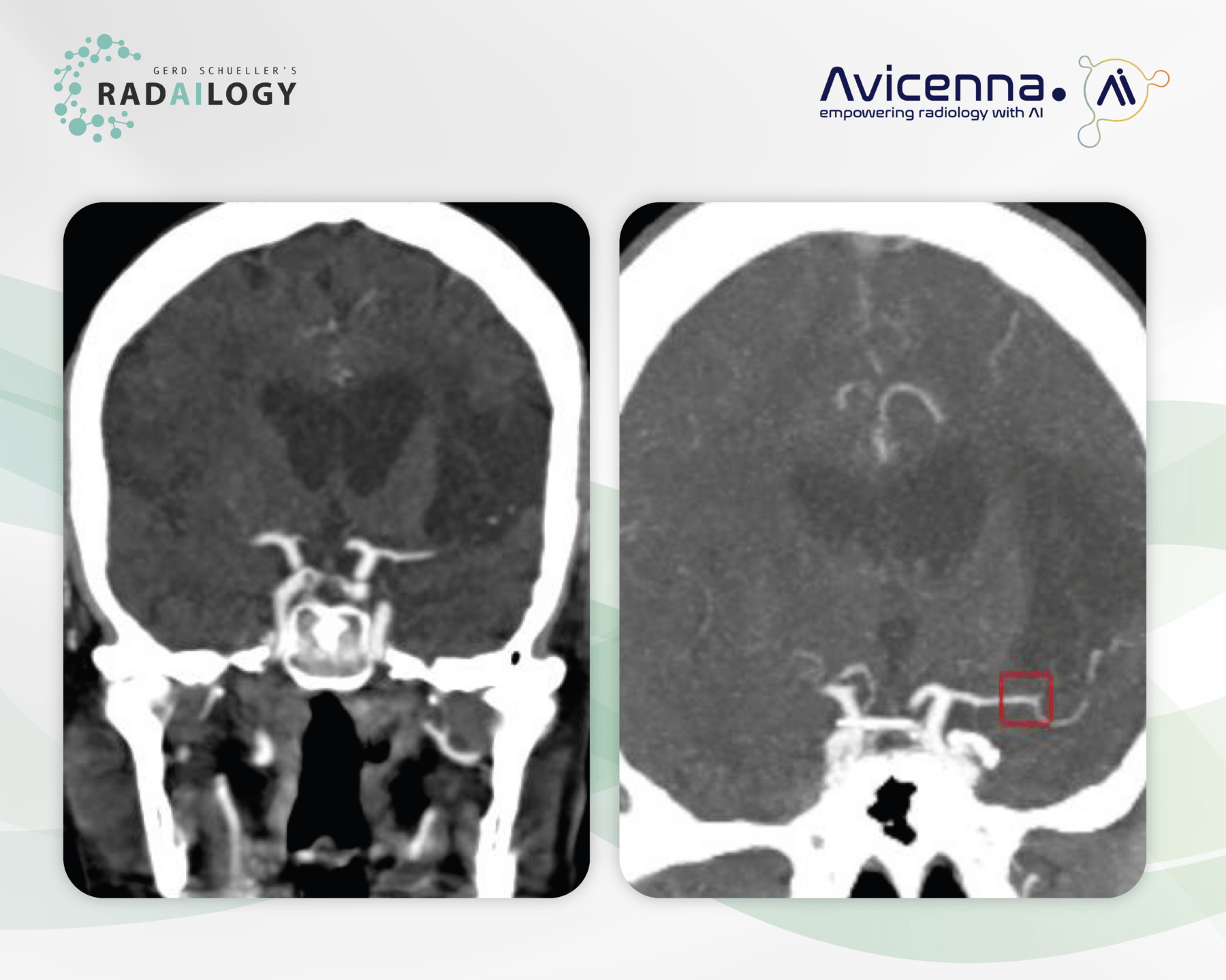
CT angiography of the skull base arteries in a 68-year-old patient with worsening right sided paresthesia. In the coronal reformation, a contrast loss of the M2 segment of the left middle cerebral artery is be seen. Peripherally adjacent there is a large older ischemic defect (left). CINA-LVO correctly detects the artery occlusion (right, red box).
Time is Health: Our motto is particularly understandable when it comes to acute ischemic strokes. In about 80% they are caused by intracranial arterial thrombi. Rapid diagnosis using CT angiography is therefore essential.
It is with great pleasure that we present CINA-LVO, an AI assistant for the detection of intracranial artery occlusion in CT angiographies.
Why CINA-LVO matters and how it works
As a triage tool for emergency radiology, CINA-LVO reports suspected acute cerebral artery occlusions in CT angiographies and enables these patients to be prioritized. The AI assistant provides radiologists and emergency physicians with clear pictures.
Any medical professional can use CINA-LVO for each individual emergency patient by quickly and easily uploading CT angiographies of the skull base arteries to Radailogy. In medical institutions, this AI assistant can also do its work automatically in the background in order to fully benefit from its triage potential.
Who benefits
The triage of arterial ischemic strokes is essential for everyone involved, i.e., patients, clinicians and radiologists.
Our own experience at Radailogy
CINA-LVO (Large vessel occlusion) detects occlusions of the distal intracranial internal carotid artery and the M1 and M2 segments of the middle cerebral artery in CT angiographies of the skull base arteries. The suspected arteries are indicated in axial and coronal MIPs.
We were able to understand most of the statistical data given by the developer for sensitivity of 97.9%, specificity of 97.6% and accuracy of 97.7%. This correlates with the developer’s statement that occlusions less than 1.5mm are not recognized.
It is reasonable to use CINA-LVO together with CINA-ICH and CINA-ASPECTS, which were developed to detect hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic strokes in CT studies. Find out more in our AI assistants!
The scientific evidence
McLouth J, Elstrott S, Chaibi Y, Quenet S, Chang PD, Chow DS, Soun JE. Validation of a Deep Learning Tool in the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage and Large Vessel Occlusion. Front Neurol. 2021 Apr 29;12:656112.
Rava RA, Peterson BA, Seymour SE, Snyder KV, Mokin M, Waqas M, Hoi Y, Davies JM, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Ionita CN. Validation of an artificial intelligence driven large vessel occlusion detection algorithm for acute ischemic stroke patients. Neuroradiol J. 2021 Oct;34(5):408-417.
Schlossman J, Ro D, Salehi S, Chow D, Yu W, Chang PD, Soun JE. Headto head comparison of commercial artificial intelligence solutions for detection of large vessel occlusion at a comprehensive stroke center. Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 10;13:1026609.
Data to upload to Radailogy
CT angiographies of the skull base arteries of any CT scanner; axial reformations; minimal matrix size 512 x 512; maximal slice thickness 1.25 mm; tube current 80 kVp to 140 kVp (recommended 120 kVp to 140 kVp); 100 to 400 mAs; artery reconstruction kernel