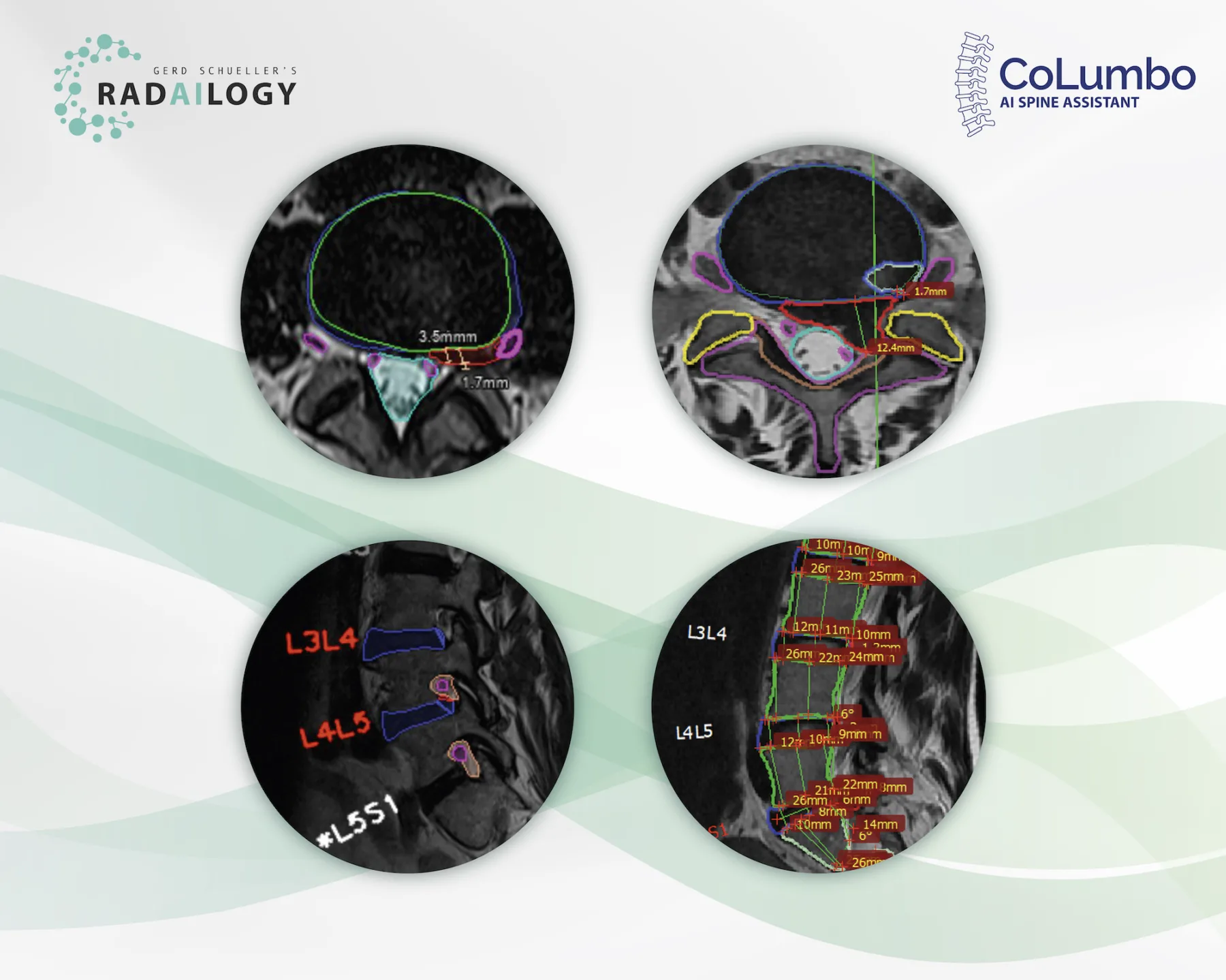
T2 axial (upper left) and T2 sagittal (lower left) MRI of the lumbar spine of a patient with back pain, lower limb weakness and paresthesia. Left foraminal disc extrusion (red) at the level L4/L5 with impingement of the left L4 nerve (pink) and discrete recessal displacement of the left L5 nerve root (pink). T2 axial (upper right) and T2 sagittal (lower right) MRI of a patient with left lower limb weakness and severe back pain. Left paramedian disc herniation (red), dural sac compression (light blue), recessal displacement of the left L5 nerve root (pink). No foraminal nerve compression (pink). Grade I retrolisthesis.
The MRI of the lumbar spine is one of the most common radiological examinations. Four out of five people will have it at some point in their lives. The most important success factors for any optimal therapy are the precision in reporting and the transmission of the results from radiologists to patients and clinicians.
It is with great pleasure that we present CoLumbo, an AI assistant for MRI of the lumbar spine.
What CoLumbo is and how it works
CoLumbo saves time and increases accuracy in the detection of the most common pathologies of the lumbar spine.
Lumbar spine MRI findings are reported and visualized. It assists in the knowledge transfer from radiologists to both patients and clinicians. In addition, all findings are written in comprehensive, standardized reports and can be used as an integral, automatically filling part of final documents.
Who benefits
Patients, clinicians, and radiologists by more detailed and more accurate diagnosis with subsequent decreased likelihood of suboptimal therapy or surgery. Accurate automatic measurements and clear colorful depiction reduce the need for measuring MRI findings by hand.
Our own experience at Radailogy
We have scrunitely studied CoLumbo over many months. Here we share some of our results with you:
This AI assistant supports the detection of disc herniation, disc bulging, central spinal stenosis, nerve root impingement, reduced vertebral and disk height, hypo- and hyperlordosis as well as spondylolisthesis and pseudolisthesis. With the actual CoLumbo version, we recommend the specialist´s review of foraminal nerve root impingement.
The scientific evidence
CoLumbo´s performance has been tested in clinical research with excellent results in accuracy for intervertebral disc detection and labeling (100%), for the detection of disc herniation (87%; 95% CI: 0.84, 0.89), extrusion (86%; 95% CI: 0.84, 0.89), bulging (76%; 95% CI: 0.73, 0.78), spinal canal stenosis (98%; 95% CI: 0.97, 0.99), nerve root compression (91%; 95% CI: 0.89, 0.92), and spondylolisthesis (87.61%; 95% CI: 85.26, 89.21), respectively.
Lehnen NC, Haase R, JFaber J, Rüber T, Vatter H, Radbruch A, Schmee FC. Detection of Degenerative Changes on MR Images of the Lumbar Spine with a Convolutional Neural Network: A Feasibility Study. Diagnostics 2021; 19;11(5):902
Data to upload to Radailogy
1.0-3.0 Tesla MRI, T2 axial and sagittal 2D and 3D, slice thickness 3.45-5 mm